Design patterns concepts
Creational
Creational patterns are ones that create objects, rather than having to instantiate objects directly. This gives the program more flexibility in deciding which objects need to be created for a given case.
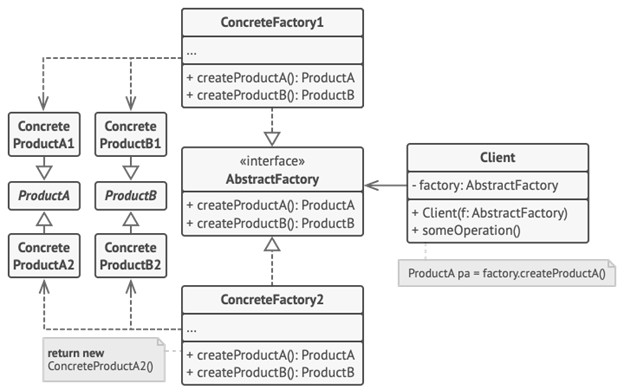
Abstract factory
Groups object factories that have a common theme.
The abstract factory pattern is a design pattern that allows for the creation of groups of related objects without the requirement of specifying the exact concrete classes that will be used. One of a number of factory classes generates the object sets.
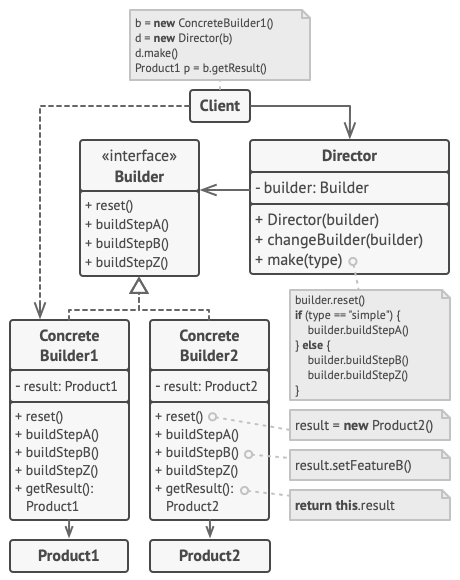
Builder
Constructs complex objects by separating construction and representation.
The builder pattern is a design pattern that allows for the step-by-step creation of complex objects using the correct sequence of actions. The construction is controlled by a director object that only needs to know the type of object it is to create.
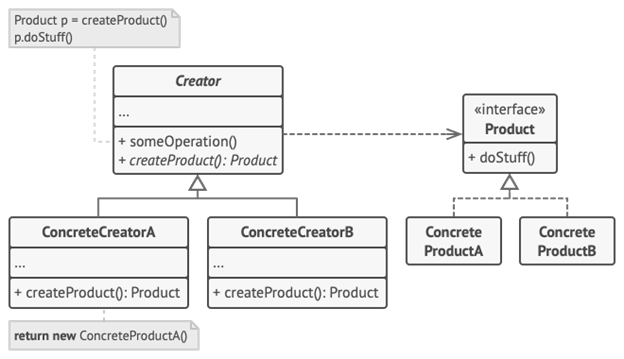
Factory method
The factory method pattern is a design pattern that allows for the creation of objects without specifying the type of object that is to be created in code. A factory class contains a method that allows determination of the created type at run-time.
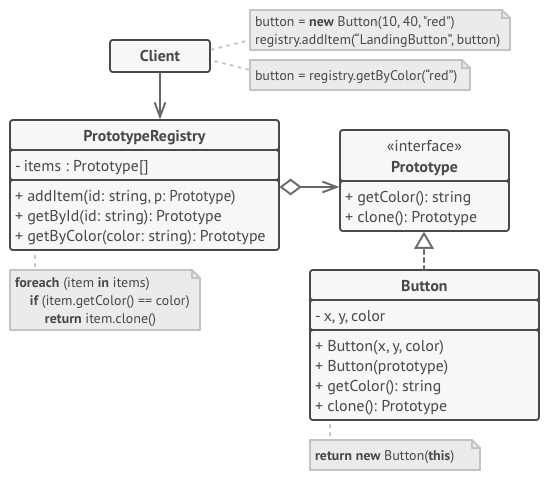
Prototype
Creates objects by cloning an existing object.
The prototype design pattern is a design pattern that is used to instantiate a class by copying, or cloning, the properties of an existing object. The new object is an exact copy of the prototype but permits modification without altering the original.
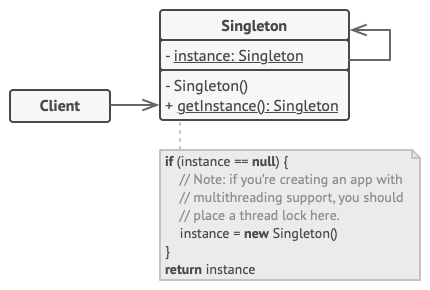
Singleton
Restricts object creation for a class to only one instance.
The singleton pattern is a design pattern that is used to ensure that a class can only have one concurrent instance. Whenever additional objects of a singleton class are required, the previously created, single instance is provided.
Structural
These concern class and object composition. They use inheritance to compose interfaces and define ways to compose objects to obtain new functionality.
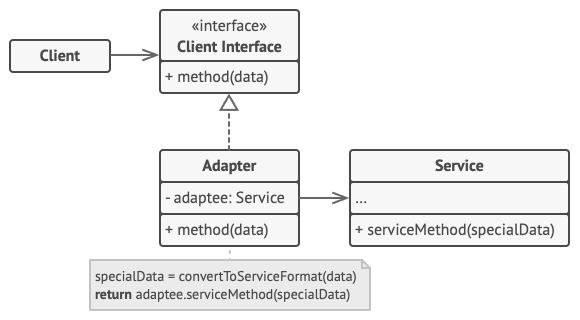
Adapter
Allows classes with incompatible interfaces to work together by wrapping its own interface around that of an already existing class.
The adapter pattern is a design pattern that is used to allow two incompatible types to communicate. Where one class relies upon a specific interface that is not implemented by another class, the adapter acts as a translator between the two types.
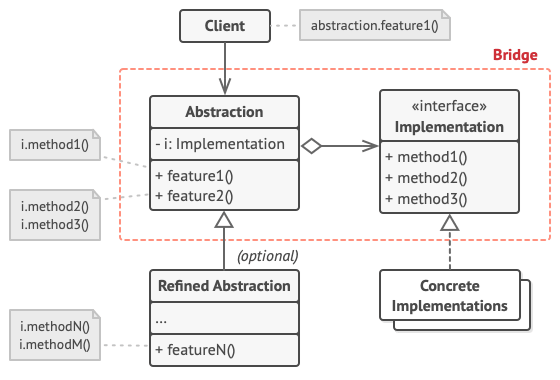
Bridge
Decouples an abstraction from its implementation so that the two can vary independently.
The bridge pattern is a design pattern that separates the abstract elements of a class from its technical implementation. This provides a cleaner implementation of real-world objects and allows the implementation details to be changed easily.
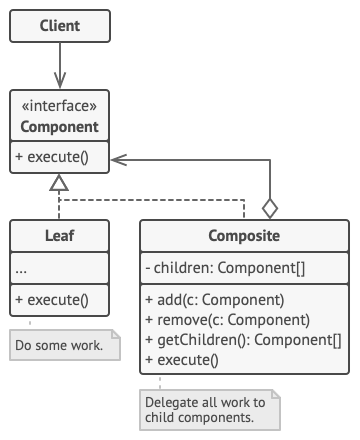
Composite
Composes zero-or-more similar objects so that they can be manipulated as one object.
The composite pattern is a design pattern that is used when creating hierarchical object models. The pattern defines a manner in which to design recursive tree structures of objects, where individual objects and groups can be accessed in the same manner.
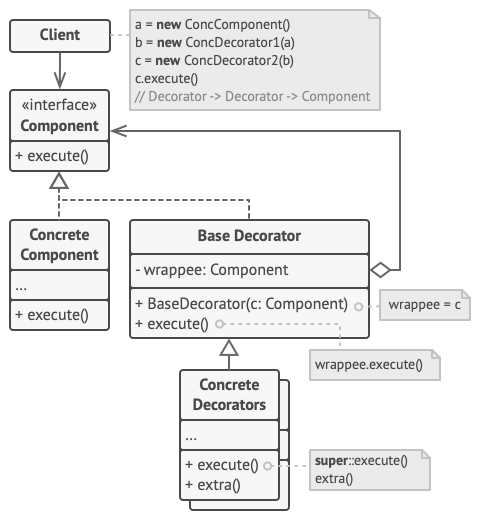
Decorator
Dynamically adds/overrides behaviour in an existing method of an object.
The decorator pattern is a design pattern that extends the functionality of individual objects by wrapping them with one or more decorator classes. These decorators can modify existing members and add new methods and properties at run-time.
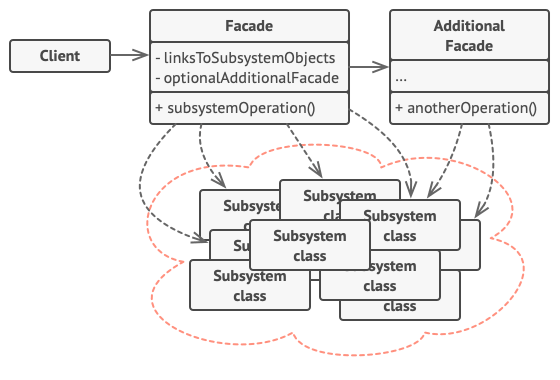
Facade
provides a simplified interface to a large body of code.
The facade pattern is a design pattern that is used to simplify access to functionality in complex or poorly designed subsystems. The facade class provides a simple, single-class interface that hides the implementation details of the underlying code.
Flyweight
reduces the cost of creating and manipulating a large number of similar objects.
The flyweight pattern is a design pattern that is used to minimize resource usage when working with very large numbers of objects. When creating many thousands of identical objects, stateless flyweights can lower the memory used to a manageable level.

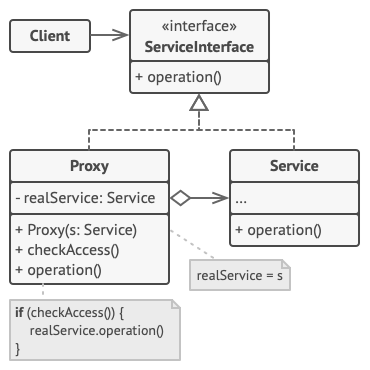
Proxy
provides a placeholder for another object to control access, reduce cost, and reduce complexity.
Proxy in a most general form is an interface to something else (Subject class). Proxy can be used when we don’t want to access to the resource or subject directly because of some base of permissions or if we don’t want to expose all of the methods of subject class. In some cases, proxies can add some extra functionality. Using proxies is very helpful when we need to access resources which are hard to instantiate, are slow to execute or are resource sensitive.
Behavioral
Most of these design patterns are specifically concerned with communication between objects.
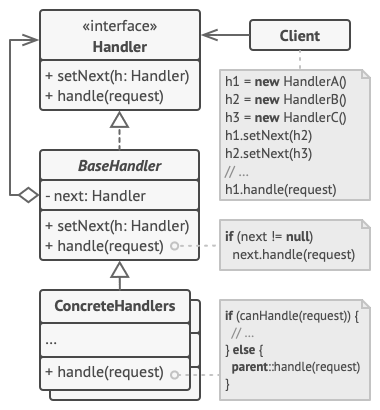
Chain of responsibility
delegates commands to a chain of processing objects.
The chain of responsibility pattern is a design pattern that defines a linked list of handlers, each of which is able to process requests. When a request is submitted to the chain, it is passed to the first handler in the list that is able to process it.
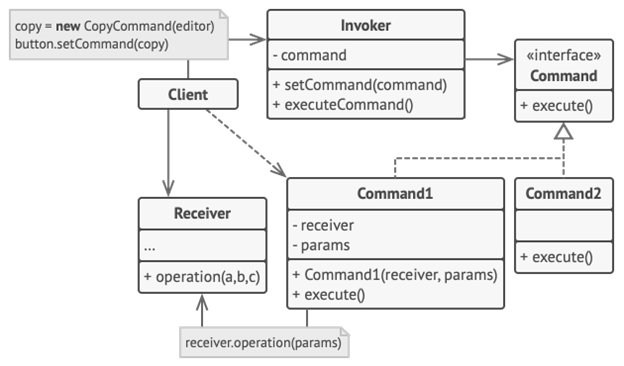
Command
creates objects that encapsulate actions and parameters.
The command pattern is a design pattern that enables all of the information for a request to be contained within a single object. The command can then be invoked as required, often as part of a batch of queued commands with rollback capabilities.
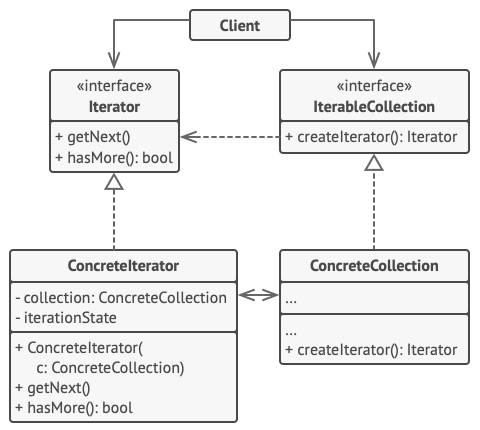
Iterator
accesses the elements of an object sequentially without exposing its underlying representation.
The iterator pattern is a design pattern that provides a means for the elements of an aggregate object to be accessed sequentially without knowledge of its structure. This allows traversing of lists, trees and other structures in a standard manner.
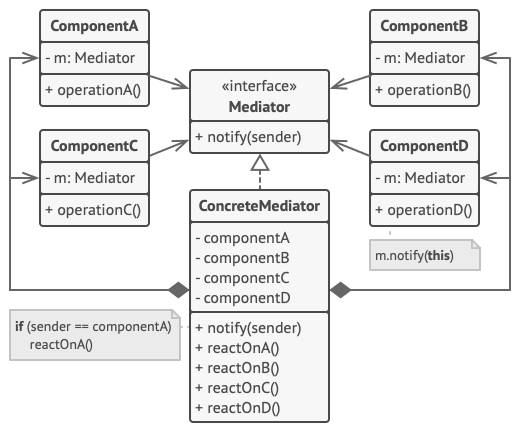
Mediator
allows loose coupling between classes by being the only class that has detailed knowledge of their methods.
The mediator pattern is a design pattern that promotes loose coupling of objects by removing the need for classes to communicate with each other directly. Instead, mediator objects are used to encapsulate and centralize the interactions between classes.
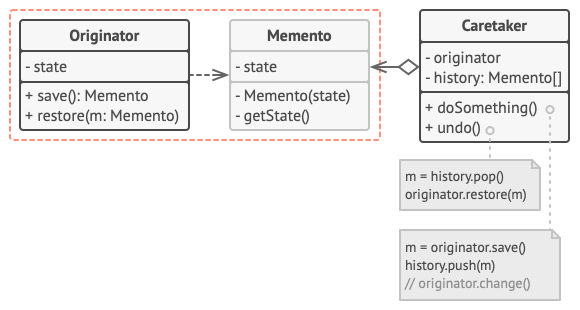
Memento
provides the ability to restore an object to its previous state (undo).
The memento pattern is a design pattern that permits the current state of an object to be stored without breaking the rules of encapsulation. The originating object can be modified as required but can be restored to the saved state at any time.
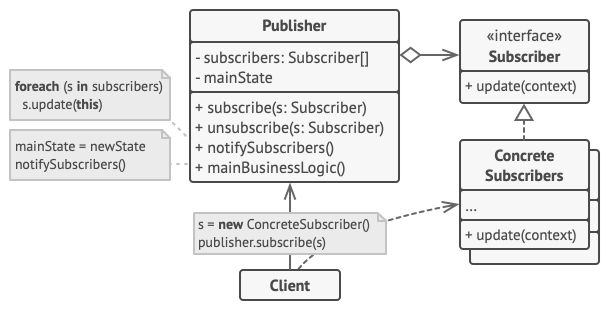
Observer
is a publish/subscribe pattern, which allows a number of observer objects to see an event.
The observer pattern is a design pattern that defines a link between objects so that when one object's state changes, all dependent objects are updated automatically. This pattern allows communication between objects in a loosely coupled manner.
State
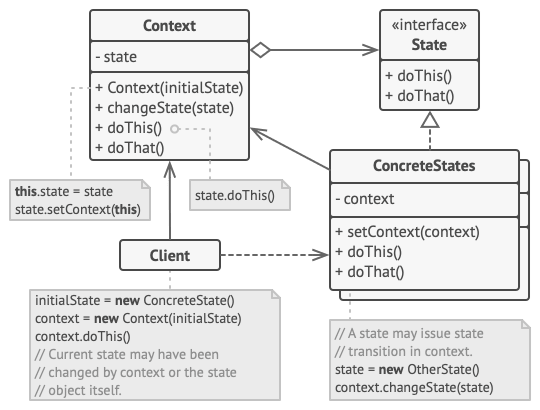
allows an object to alter its behavior when its internal state changes.
The state pattern is a design pattern that allows an object to completely change its behavior depending upon its current internal state. By substituting classes within a defined context, the state object appears to change its type at run-time.
Strategy
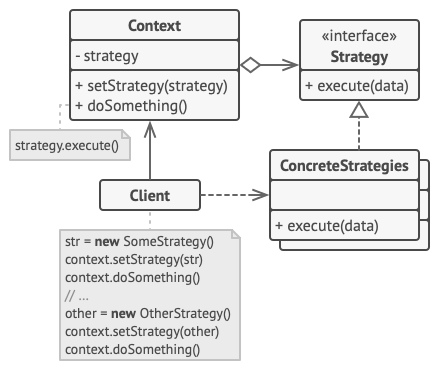
Allows one of a family of algorithms to be selected on-the-fly at runtime.
The strategy pattern is a design pattern that allows a set of similar algorithms to be defined and encapsulated in their own classes. The algorithm to be used for a particular purpose may then be selected at run-time according to your requirements.
Template
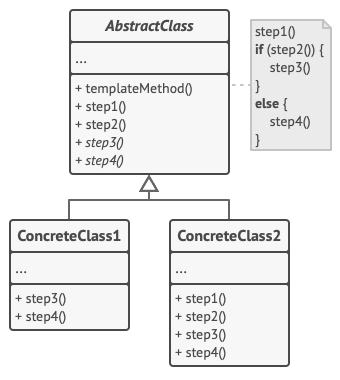
method defines the skeleton of an algorithm as an abstract class, allowing its subclasses to provide concrete behavior.
The template method pattern is a design pattern that allows a group of interchangeable, similarly structured, multi-step algorithms to be defined. Each algorithm follows the same series of actions but provides a different implementation of the steps.
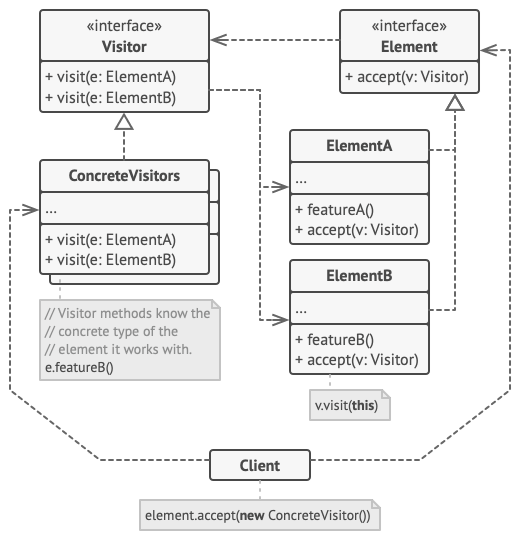
Visitor
separates an algorithm from an object structure by moving the hierarchy of methods into one object.
The visitor pattern is a design pattern that separates a set of structured data from the functionality that may be performed upon it. This promotes loose coupling and enables additional operations to be added without modifying the data classes.
References: